Phylogenetic observation in Ariidae, Bagridae and Plotosidae catfishes by COI gene sequence analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15835/nsb12410822Keywords:
catfish; cytochrome oxidase I; monophyly; phylogeny; transition; transversionAbstract
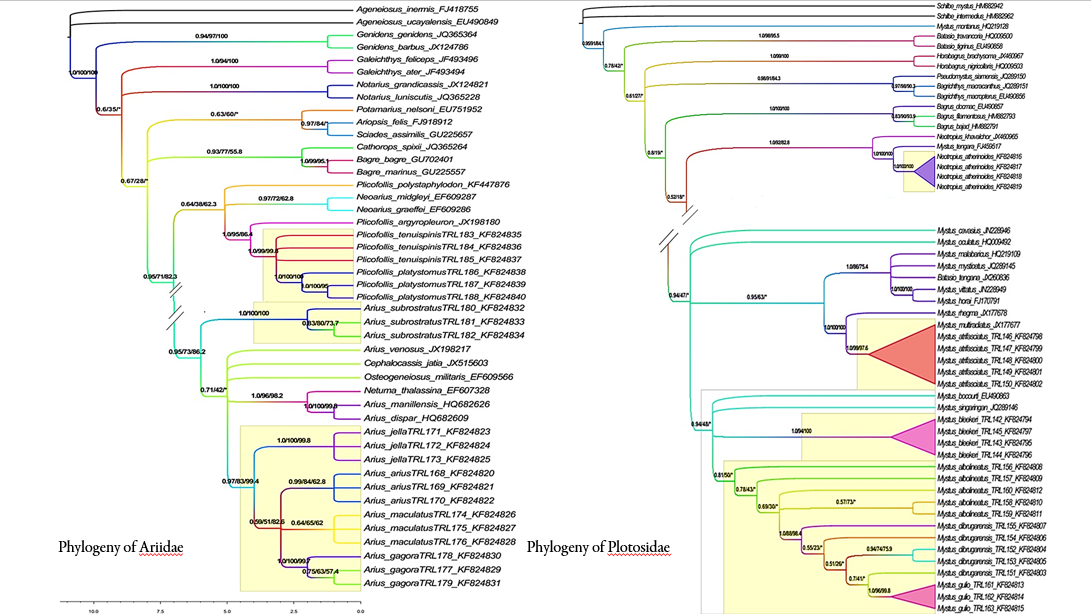
To understand the phylogenetic status of Ariidae, Bagridae and Plotosidae catfishes, this study was planned using the barcode gene, cytochrome oxidase I (COI). Totally 71 species were used in phylogenetic reconstructions under maximum parsimony, maximum likelihood and Bayesian inference criteria. The one-way ANOVA showed that the three catfish families are significantly different (F= 19.79, d.f. = 3; 116, P< 0.0001 (Plotosidae); F= 44.21, d.f.= 3; 986, P< 0.0001 (Ariidae); F= 24.83, d.f.= 3; 1322, P< 0.0001 (Bagridae). In MP, ML and BI based phylogenetic tree of Ariidae, Plicofollis genus displayed as a monophyletic group with higher bootstrap and posterior probability values for all the species except two species of Neoarius, which intervened separating P. polystaphylodon. In the phylogenetic tree of Plotoside, Plotosus genus displayed as monophyletic group with higher bootstrap and posterior probability values for all the eight species. In the case of Bagridae phylogeentic tree, Mystus genus displayed as a monophyletic group with higher bootstrap and posterior probability values for all the species except Mystus montanus forming a distant and distinct clade whereas Mystus tengara collides into monophyletic clade when Neotropius genuswas removed. By this study we could establish a phylogenetic hypothesis for all the 36 catfish families and examine the monophyly status of the subfamilies and genera.
Metrics
References
Acero PA, Betancur RR (2007). Monophyly, affinities, and subfamilial clades of sea catfishes (Siluriformes: Ariidae). Ichthyological Exploration of Freshwaters 18:133-143.
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research 25:3389-3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Bensasson D, Zhang DX, Hartl DL, Hewitt GM (2001). Mitochondrial pseudogenes: evolution's misplaced witnesses. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 16:314-321. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-5347(01)02151-6
Betancur RR (2009). Systematics and evolutionary history of sea catfishes (Siluriformes: Ariidae). In: Ph.D. Thesis, Auburn University, Auburn pp 200.
Booth AJ, Muwanika VB, Masembe C, Nyakaana S, Rutaisire J (2004). Evolution of Labeo victorianus predates the Pleistocene desiccation of Lake Victoria: Evidence from mitochondrial DNA sequence variation. South African Journal of Science 100:607-608.
Brown JM, Pellmyr O, Thompson JN, Harrison RG (1994). Mitochondrial DNA phylogeny of the Prodoxidae (Lepidoptera: Incurvarioidea) indicates rapid ecological diversification of Yucca moths. Annals of Entomological Society of America 87:795-802. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/87.6.795
Dowton M, Austin AD (1997). Evidence for AT-transversion bias in wasp (Hymenoptera: Symphyta) mitochondrial genes and its implications for the origin of parasitism. Journal of Molecular Evolution 44:398-405. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006159
Drummond AJ, Ho SYW, Rawlence N, Rambaut A (2007). A rough guide to BEAST 1.4. University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh pp 1-41.
Duftner N, Koblmuller S, Sturmbauer C (2005). Evolutionary relationships of the Limnochromini, a tribe of benthic deep-water cichlid fish endemic to Lake Tanganyika, East Africa. Journal of Molecular Evolution 60:277-289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-004-0017-8
Frati F, Simon C, Sullivan J, Swofford DL (1997). Evolution of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase II gene in Collembola. Journal of Molecular Evolution 44:145-158. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006131
Hebert P, Cywinska A, Ball S, Dewaard J (2003). Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 270:313-321. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2002.2218
Howland DE, Hewitt GM (1995). Phylogeny of the Coleoptera based on mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I sequence data. Insect Molecular Biology 4:203-215. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2583.1995.tb00026.x
Jayaram KC (1984) Ariidae. In: Fischer W, Bianchi G (Eds.), Western Indian Ocean Fishing area 51.1. FAO, Rome.
Knowlton N, Weigt LA (1998). New dates and new rates for the divergence across the Isthmus of Panama. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 265:2257-2263. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.1998.0568
Kumar S, Gadagkar SR (2001). Disparity index: A simple statistic to measure and test the homogeneity of substitution patterns between molecular sequences. Genetics 158:1321-1327.
Machordom A, Macpherson E (2004). Rapid radiation and cryptic speciation in squat lobsters of the genus Munida (Crustacea, Decapoda) and related genera in the South West Pacific: molecular and morphological evidence. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 33:259-279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2004.06.001
Mardulyn P, Whitfield JB (1999). Phylogenetic signal in the COI, 16S and 28S genes for inferring relationships among genera of Microgastrinae (Hymeoptera; Braconidae): Evidence of a high diversification rate in this group of parasitoids. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 12:282-294. https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.1999.0618
Miura T, Maekawa K, Kitade O, Abe T, Matsumoto T (1998). Phylogenetic relationships among subfamilies in higher termites (Isoptera: Termitidae) based on mitochondrial COII gene sequences. Annals of Entomological Society of America 91:515-523.
Moritz C, Cicero C (2004). DNA barcoding: Promise and pitfalls. PLoS Biology 2:e354. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0020354
Mourier T, Hansen AJ, Willerslev E, Arctander P (2001). The human genome project reveals a continuous transfer of large mitochondrial fragments to the nucleus. Molecular Biology and Evolution 18:1833-1837. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003971
Page TJ, Hughes JM (2010). Comparing the performance of multiple mitochondrial genes in the analysis of Australian freshwater fishes. Journal of Fish Biology 77:2093-2122. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2010.02821.x
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998). Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817-818. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.817
Remigio E, Hebert P (2003). Testing the utility of partial CO1 sequences for phylogenetic estimates of gastropod relationships. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 29:641-647. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1055-7903(03)00140-4
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003). MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572-1574. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. 2nd Edition. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbour, New York, pp 1626.
Santos BS, Quilang JP (2011). DNA barcoding of Arius species (Siluriformes: Ariidae) in Laguna de Bay, Philippines using the cytochrome C oxidase subunit I gene. Philippine Agricultural Scientist 94:205-210.
Stamatakis A (2006). RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688-2690. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btl446
Sullivan JP, Lundberg JG, Hardman M (2006). A phylogenetic analysis of the major groups of catfishes (Teleostei: Siluriformes) using rag1 and rag2 nuclear gene sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 41:636-662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2006.05.044
Swofford DL (2002). PAUP: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony, Version 4.0 Beta. Sinauer Associates Inc., Sunderland, MA, USA.
Talwar PK, Jhingran AG (1991). Inland fisheries of India and adjacent countries. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi, India, pp 514.
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011). MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution 28:2731-2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Ward RD, Zemlak TS, Innes BH, Last PA, Hebert PDN (2005). DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philosophical Transactions Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 360(1462):1847-1857. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2005.1716
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Papers published in Notulae Scientia Biologicae are Open-Access, distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
© Articles by the authors; licensee SMTCT, Cluj-Napoca, Romania. The journal allows the author(s) to hold the copyright/to retain publishing rights without restriction.
License:
Open Access Journal - the journal offers free, immediate, and unrestricted access to peer-reviewed research and scholarly work, due SMTCT supports to increase the visibility, accessibility and reputation of the researchers, regardless of geography and their budgets. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.













.png)















